Vehicle insurance, also known as auto insurance or car insurance, is a contract between the vehicle owner and an insurance company that provides financial protection against various risks associated with owning and operating a vehicle. Here’s a detailed description:
Key Components of Vehicle Insurance
- Coverage Types:
- Liability Coverage: Covers damages to other people and their property if you’re at fault in an accident. It usually includes:
- Bodily Injury Liability: Pays for medical expenses, lost wages, and legal fees for injuries to others.
- Property Damage Liability: Covers repair or replacement costs for someone else’s property (like a vehicle or fence).
- Collision Coverage: Pays for damages to your own vehicle resulting from a collision, regardless of fault.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Covers non-collision-related incidents, such as theft, vandalism, natural disasters, and animal collisions.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): Covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of fault. It may also cover lost wages and other related costs.
- Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: Protects you if you’re in an accident with a driver who has no insurance or insufficient coverage.
- Factors Affecting Premiums:
- Driving History: Your record of accidents, claims, and traffic violations.
- Vehicle Type: Make, model, age, and safety features of your car.
- Location: Where you live and park your vehicle can affect risk levels (e.g., urban vs. rural).
- Age and Gender: Younger drivers or certain gender demographics may face higher premiums due to statistical risk.
- Credit History: In some regions, insurers use credit scores as a factor in determining premiums.
- Policy Limits:
- Policies specify coverage limits, which is the maximum amount the insurer will pay in the event of a claim. Higher limits typically result in higher premiums.
- Deductibles:
- This is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance kicks in. Higher deductibles usually mean lower premiums, but you’ll pay more in the event of a claim.
- Exclusions:
- Specific situations or conditions that are not covered by the policy, such as wear and tear, driving under the influence, or using the vehicle for commercial purposes.
- Additional Coverage Options:
- Roadside Assistance: Services like towing, tire changes, and lockout assistance.
- Rental Car Reimbursement: Covers costs for a rental car while your vehicle is being repaired.
- Gap Insurance: Covers the difference between what you owe on your car loan and its current market value in case of a total loss.
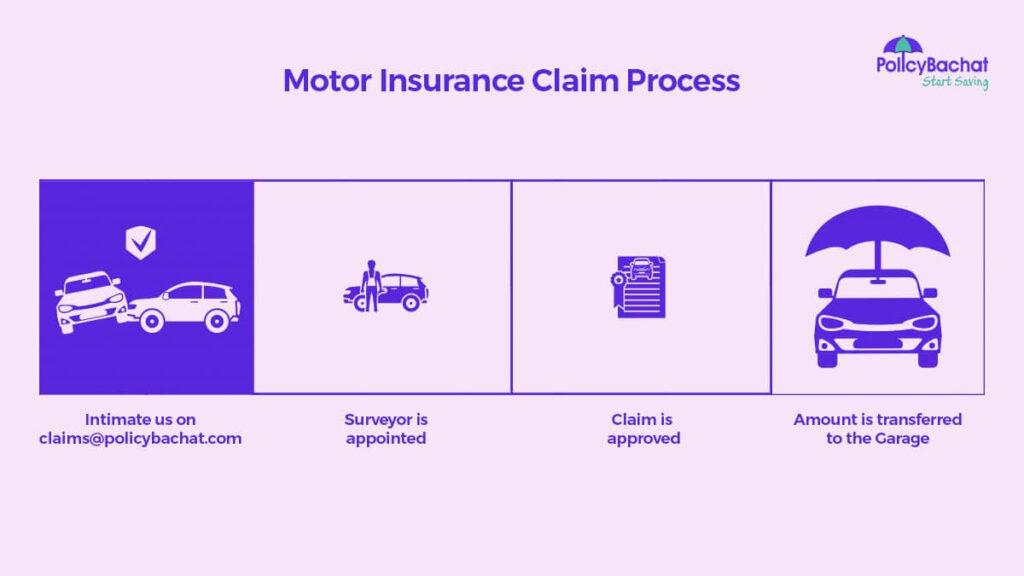
Claims Process
- Report the Incident: Notify your insurance company as soon as possible after an accident or loss.
- Claim Assessment: The insurer investigates the claim, which may include gathering statements, police reports, and estimates for repairs.
- Settlement: Once the claim is approved, the insurer will pay for covered damages up to the policy limits, minus any deductibles.
Importance of Vehicle Insurance
- Financial Protection: Helps cover costs associated with accidents, injuries, and property damage, preventing significant out-of-pocket expenses.
- Legal Requirement: In many places, having a minimum level of liability insurance is mandated by law.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing you are covered can reduce stress and anxiety related to driving.
Conclusion
Vehicle insurance is an essential aspect of responsible vehicle ownership, providing crucial financial protection against a variety of risks. Understanding the different types of coverage, how premiums are determined, and the claims process can help you make informed decisions about your auto insurance needs.

